
The Ultimate Guide to Payroll and Compliance in India [2025 Edition]
Mistakes in maintaining statutory compliance in payroll are a sore spot for several Indian companies. It costs them millions every single year in the form of crippling mandatory fines and a lack of trust from employees.
With the endless update cycle of labour laws, audits, GST changes, and new digital reporting techniques that need to be followed, even the slightest mistake in the payroll and compliance process can result in legal repercussions.
In this comprehensive guide on payroll compliance in India, you'll discover how to make this seemingly complex process surprisingly doable, by getting a bird's eye view into:
- Mandatory statutory requirements in the payroll framework
- Month-by-month payroll compliance calendars
- Proven best practices for staying audit-ready
- And modern tech solutions to automate payroll processing
What Is Payroll Compliance?
Payroll compliance refers to the state where an organisation (employer) is paying salaries to their employees as per the statutory requirements, such as the Minimum Wage Act, mandatory contributions (like EPF, ESI), record maintenance and tax deductions. But beyond just meeting these legal requirements, payroll and compliance play a pivotal role in keeping the reputation of the company.
A company that fails to comply with payroll statutory compliance India won't just lose the trust of its employees. It will risk being flagged by competitors, penalised by authorities, and could eventually land on the government's defaulter list. So, it's imperative to wrap your head around the full scope of payroll compliance meaning with a strong grasp of what's at stake if you slip up.
Why Does Payroll Compliance Matter in 2025?
As we talk about payroll compliance in India in 2025, its criticalness is rooted in four different labour codes: wages, occupational safety, social security and industrial relations. These four codes have been brought into place after unifying 29 laws that existed prior to that.
As per these codes, there is a minimum wage requirement that employers must comply with, which varies by state, ranging from ₹178 to ₹528/day. Also, there is a mandate for a PF contribution amounting to 12% of the employee's basic wages, along with ESIC coverage for eligible small businesses.
All these have a huge influence on the payroll administration procedure. Hence, it is non-negotiable for companies to verify their accurate compliance with these provisions.
Non-compliance can result in fines, for instance, if the wage code is breached, 7% interest on late PF deposits, and reputational damage impacting MSME credibility. In recent years, there has been an increase in the frequency of audits by EPFO and GST authorities targeting misclassification and tax errors. Automated payroll tools and expert audits are essential to navigate complexities, avoid penalties, and ensure trust.
Key Payroll and Compliance Acts Applicable for Businesses in India in 2025
| Act | Applicability | Action Required |
|---|---|---|
| Payment of Wages Act, 1936 | All Businesses/Establishments | Make sure that the salary is disbursed on time without any unauthorised deductions |
| Minimum Wages Act, 1948 | Sector-wise and state-specific | Pay notified minimum wages (₹178–₹528/day as per state) |
| Employees' Provident Fund & Misc. Provisions Act, 1952 | Companies employing 20 or more workers | A 12% share of the basic wage is to be contributed separately by both the employer and the employee. |
| Employees' State Insurance Act, 1948 | Establishments with 10+ employees earning ≤ ₹21,000/month | Employer: 3.25% and Employee: 0.75% of gross wages |
| Income Tax Act, 1961 | All salaried employees | Deduct TDS from salaries based on tax slabs and deposit it monthly |
| Professional Tax | Applicable in select states | Deduct monthly as per slab and remit to state government |
| Payment of Bonus Act, 1965 | Establishments with 10+ employees | Pay annual bonus (8.33%–20%) to eligible employees |
| Payment of Gratuity Act, 1972 | Upon the maturity of 5 years of continuous employment | Pay 15 days' wages per completed year of service upon exit |
| Labour Welfare Fund | State-specific, mandatory in select states | Employer and employee contribute as per state rules (e.g., ₹6/₹12 etc.) |
2025 Payroll Compliance Calendar
Below is the detailed timeline to maintain statutory compliance in payroll for your business in India for the year 2025.
| Month | Payroll Compliance Checklist in India (PF, ESI, PT, TDS, Form‑16, Challans) |
|---|---|
| January | PF/ESI challans by 15th Feb; PT payment (varies by state, often by 20th); TDS payment by 7th Feb. |
| February | Settle PF and ESI dues by March 15th; for PT and TDS, aim for the 20th and 7th respectively. |
| March | PF/ESI by 15th Apr; PT by ~20th; TDS by 7th Apr; Annual PT Return (if applicable in your state). |
| April–June (Q1) | PF/ESI deposits by the 15th of next month; TDS payments by the 7th of each month; TDS quarterly return (24Q) by 31st July. |
| July | PF/ESI by 15th Aug; PT by ~20th; TDS by 7th Aug; Form 16 due by 15th July. |
| August | PF/ESI by 15th Sep; PT by ~20th; TDS by 7th Sep. |
| September | PF/ESI by 15th Oct; PT by ~20th; TDS by 7th Oct; Q2 TDS return (24Q) by 31st Oct. |
| October | 15th Nov for PF/ESI. TDS and PT by the 7th and 20th, respectively. |
| November | PF/ESI by 15th Dec; PT by ~20th; TDS by 7th Dec. |
| December | PF/ESI by 15th Jan; PT by ~20th; TDS by 7th Jan; Q3 TDS return by 31st Jan. |
Key Highlights (As Per India Payroll Compliance 2025):
Monthly Filings
The following monthly filings need to be completed on time. As it's a legal requirement, make sure you prioritise their timely submission.
EPF & ESIC:
EPF and ESIC contributions should be deposited no later than the 15th of the next month.
Professional Tax (PT):
Check the rules specific to your state before filing Professional Tax. These payments are generally expected to be completed by the 20th of each month.
TDS Payment:
Deposit TDS dues on or before the ensuing month's 7th without fail.
Quarterly TDS Returns (Form 24Q):
Below are the crucial quarterly filings for Tax Deducted at Source (TDS) that must be submitted by the following deadlines to ensure compliance.
- Q1 (Apr–Jun): by 31st July
- Q2 (Jul–Sep): by 31st October
- Q3 (Oct–Dec): by 31st January
- Q4 (Jan–Mar): by 31st May
Annual Obligations:
Form 16: Make sure you issue this to your employees by 15th June (as per Income Tax Rules and don't wait till July, as delay can cause employees to face refund delays in their tax return process.
Professional Tax Annual Return: In April, in certain states (e.g. Maharashtra).
Gratuity: Payable on employee exit as per the Payment of Gratuity Act. Although it is not a fixed “annual” return, it is still a statutory payroll and compliance criterion in India.
Is Professional Tax Applicable in Your State?

Not all Indian states levy Professional Tax. So, when configuring your payroll management system, it is crucial to verify whether Professional Tax is applicable in the state(s) where your employees are located. Here's a state-wise breakdown to help you avoid incorrect filings.
| States & UTs where Professional Tax is applicable | States & UTs where Professional Tax is not applicable |
|---|---|
| Andhra Pradesh | Arunachal Pradesh |
| Assam | Chandigarh |
| Bihar | Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu |
| Chhattisgarh | Delhi |
| Gujarat | Goa |
| Jharkhand | Haryana |
| Karnataka | Himachal Pradesh |
| Kerala | Jammu and Kashmir |
| Madhya Pradesh | Ladakh |
| Maharashtra | Lakshadweep |
| Manipur | Andaman and Nicobar Islands |
| Meghalaya | Uttar Pradesh |
| Mizoram | Uttarakhand |
| Nagaland | |
| Rajasthan | |
| Odisha | |
| Sikkim | |
| Puducherry | |
| Punjab | |
| Tamil Nadu | |
| Telangana | |
| Tripura | |
| West Bengal |
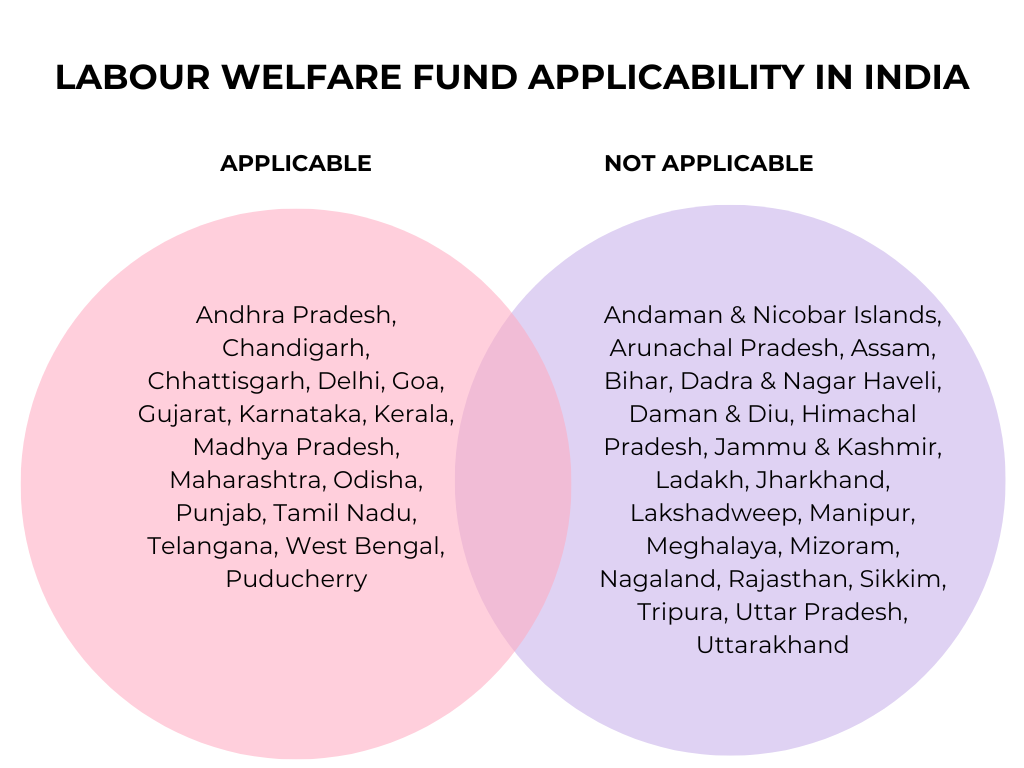
Does Your State Have a Labour Welfare Fund (LWF Requirement)?
Labour Welfare Fund (LWF) is a legal contribution collected for the welfare of employees through state-specific welfare boards. What is essential to remember here is that its scope is limited to select states in India. Each state may have different rates, timelines, rules, and contribution requirements.
As part of the payroll audit checklist, employers need to confirm if LWF applies in their state and make the required deductions and remittances on time. The Venn diagram below distinguishes between the states where LWF is applicable and those where it is not.
Statutory Best Practices for Meeting Statutory Compliance In Payroll
Automate Payroll and Compliance with a Modern System
These days, you don't have to do payroll and compliance manually. A good software does the maths without missing any important figures or causing late tax forms filing.
However, when you choose a payroll management software, it is essential to empahsize one that can bring all employee data together, pushes out real-time rule changes, and keeps a detailed trail of every adjustment like Provident Fund (PF) contributions, Employee State Insurance (ESI), Professional Tax (PT), TDS on salaries etc.
These are the manual tasks that cause payroll errors. When these very tasks are automated by payroll software for compliance India, it reduces HR's workload and provides them with clear audit trails for inspectors or anyone reviewing the records.
Regular Audits & Staff Training
Maintain an elaborate HR compliance checklist India for your internal inspection, and conduct formal checks every three months and again at year-end to spot gaps before they start costing you extra time or money.
At the same time, keep your HR crew learning about new payroll laws India 2025 and the tricky bits that show up in every update. Having a sharp and educated team to deal with the payroll and compliance-related complexities is very important for maintaining the integrity and accuracy of your statutory compliance efforts.
Staying Informed & Policy Updates
Subscribe to official feeds like Shram Suvidha that ping you the second a fresh update is announced. Pair that with trusted news sources, so you will never miss state updates and national code changes.
Also, set a clear plan for reading new updates related to payroll and compliance, making sense of them, and rolling the changes out across the office. Oftentimes, gliding through policy changes hits bumpy stops when you uncover last-minute fixes and unexpected issues. Without a defined system, you will have no clue as to how to avoid payroll penalties in India.
Role of Technology in Payroll And Compliance
 Statutory compliance in payroll can be enhanced by incorporating automated payroll software with built-in compliance checks. Here are some of the essential requirements for these tools in today's complex regulatory environment.
Statutory compliance in payroll can be enhanced by incorporating automated payroll software with built-in compliance checks. Here are some of the essential requirements for these tools in today's complex regulatory environment.- Integrated HRMS/payroll platforms
- Real-time statutory updates and alerts
- Self‑service portals for employees (Form 16 download, tax forms, etc.)
- Auto-update feature for the latest statutory rule changes
- Built-in support for PF, ESI, and TDS calculations
- State-wise compliance configurations and tax rule mapping
- Timely reminders for monthly, quarterly, and annual filings
- Quick and accurate generation of statutory forms and challans
- Audit-ready reports with traceable transaction histories
- Role-based access control for secure compliance handling
- Integration with government portals and APIs
- Alerts for due dates and compliance breaches
- Multi-location employee compliance handling in one dashboard
How to Choose the Right Payroll Software Service Provider?
As long as keeping payroll compliance in India intact, the role of the payroll management software you choose is crucial. So, choosing a system that has solid reviews and offers full audit help is paramount.
If your business operates in more than one state, it is imperative to make sure the system is capable of handling different taxes and labour rules without disruption. Also essential is the service's clear and honest pricing. You don't want to be hit by surprise bills, and you want budgeting to be easier.
Another key aspect to look into is the software's ability to accommodate the latest regulations and the level of integration it offers with your other tools, such as accounting, HRMS, and attendance systems. Payroll can't operate independently. To run it faster and in a less error-prone environment, these essential features are a must-have.
Conclusion & Next Steps
Navigating payroll and compliance in India involves more than a basic checklist. You must intimately understand key concepts like PF, ESI, and TDS and what those mean for salary processing, deductions, and filings. Progress in this area often hinges on dependable automation tools, periodic payroll compliance audits, regular training for finance teams, and a proactive approach to new circulars and amendments.
Now is a good time to take an honest look at your payroll function. Are you looking for a smart and cost-effective way to simplify payroll and compliance and avoid costly penalties? We can help!
FAQ
What happens if the EPF filing is late?
When an employer files the EPF statement after the due date, the statutory interest climbs to 12% a year and various penalties kick in, between 5% and 25%, subject to how long the delay stretches. More importantly, late submissions can stall an employee's access to benefits such as withdrawals, transfers, or pension settlements.
How is ESIC eligibility determined?
Under the ESI Act, employees earning ₹21,000 or less each month (₹25,000 for those with disabilities) must have ESIC coverage. The scheme is mandatory for businesses with at least ten staff, twenty in some states. Firms below that headcount don't have to enrol, but they can sign up voluntarily if they wish.
Is it possible to correct TDS errors post-filing?
Yes, it is possible. To fix TDS filing errors like wrong PANs, mismatched amounts or faulty challan details post-filing, prepare a revised file using the RPU tool and upload it again on the TRACES portal. Once the revised return is processed, the corrected details will override the previous errors, and any pending demands or mismatches linked to the old filing will be automatically updated.
What is regarded as statutory leave, and how can we account for it?
Statutory leave covers paid time off that employees have the right to avail such as sick, casual, and maternity leave, per the Factories or Shops Act. If you are using a standard HRMS system with an integrated payroll system, for instance, Mewurk, you can easily configure statutory leave policies, track accruals, and apply rules automatically.
Most Popular Post

Why Accurate Attendance and Leave Management Matters for Business Growth?
Read More →Why Accurate Attendance and Leave Management Matters for Business Growth?
How To Leverage Attendance Data For Better Workforce Management?
Read More →How To Leverage Attendance Data For Better Workforce Management?




