
How to Prepare for a Payroll Audit: A Step-by-Step Guide
A payroll audit can feel like an unexpected, unwelcome spotlight on your business’s financial health. In fact, it has a way of unsettling even the most confident business owners. Not because there’s misconduct, but because an audit throws sharp focus on the small details that often get rushed, like the missing signatures, misplaced timesheets, and overlooked tax adjustments.
A clear pattern has emerged over time: businesses that treat their payroll system as a living, continuously improving process tend to stay steady. They remain prepared without scrambling. And preparation is the best defence in moments like a payroll audit.
What is a Payroll Audit?
A payroll audit is a meticulous, formal examination of an organisation's payroll records, practices, and financial transactions. Its purpose is to verify that all wages, withholdings, tax filings, and employee classifications comply with federal, state, and local labour and tax laws.
For businesses operating in India, this means adherence to laws like the Income Tax Act, 1961, the Employees’ Provident Funds and Miscellaneous Provisions Act, 1952, the Employees' State Insurance Act, 1948, and various state-specific Professional Tax and Minimum Wages regulations.
Types of Payroll Audits
A payroll audit can be:
Internal:
When your finance or HR team reviews records before anyone else does.
External:
Led by agencies such as the Income Tax Department, EPFO, ESIC, or state-level labour inspectors.
Income Tax Department (ITD) Audits:
Focus on TDS (Tax Deducted at Source) compliance, Form 16/16A issuance, tax calculation on employee salaries, and filing of quarterly TDS returns (Form 24Q).
Employees' Provident Fund Organisation (EPFO) Audits:
Scrutinise whether all eligible employees are enrolled in the EPF scheme, the correct contribution rate (typically 12% of Basic + Dearness Allowance) is being applied by both employer and employee, and timely remittance via ECR (Electronic Challan cum Return).
Employees’ State Insurance Corporation (ESIC) Audits:
Check compliance for employees whose gross monthly wages fall below the prescribed ceiling, ensuring the right contribution is deducted and paid.
Labour Department Audits:
Initiated as a result of employee complaints and focuses on compliance with the Minimum Wages Act, Payment of Wages Act, and regulations concerning overtime pay and leave.
Regulatory:
Like PF audits, shop and establishment inspections, or professional tax reviews.
Trigger-based:
When inconsistencies show up in tax filings, employee complaints, or mismatched returns.
Why Should a Business Run Regular Payroll Audits?
A payroll that looks fine on the surface may still have issues underneath. Running regular, internal payroll compliance audits is an essential component of responsible business governance, especially in the evolving landscape of Indian labour codes. Regular payroll audits reduce the probability of:
Penalties and Fines for Non-Compliance:
The financial consequences of non-compliance can be severe. For instance, delays in depositing TDS or EPF can attract heavy interest and penalties. The cost of rectifying a past error, along with penalties, is almost always higher than the cost of prevention.
Payroll errors with financial risk:
Catching a systemic error like incorrect calculation of overtime for non-exempt employees or misapplied Professional Tax rates today can save you from massive liability tomorrow across the entire workforce and multiple years.
Employee Trust Risks from Payroll Mistakes:
The primary motive of any employee to work for an organisation is their compensation. And nothing can damage their trust in you than incorrect pay. Ensuring timely and accurate salary, leave, and benefit disbursements, verified by a robust audit process, helps employees feel secure about what they’re owed and confident that the organisation values their work.
Maintaining Regulatory Compliance:
In India, maintaining compliance with the myriad of central and state laws requires constant vigilance. Regular audits ensure your business stays ahead of legislative changes, such as those related to the proposed Code on Wages.
Common Red Flags That Trigger Payroll Audits
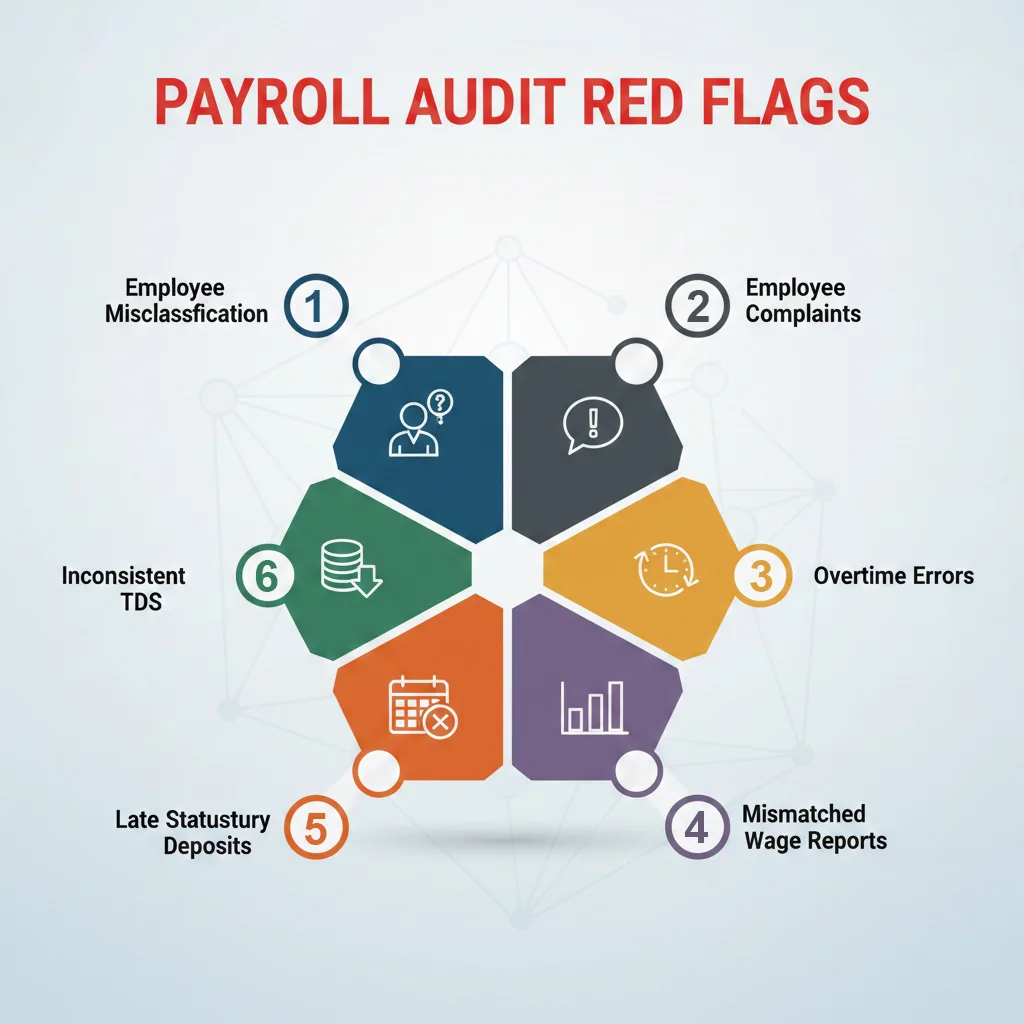
If you notice any of the below scenarios in your organisation, it is a clear sign that you must immediately do an internal audit of payroll process.
Misclassification of Employees vs. Contractors:
The misuse of independent contractors to avoid mandatory contributions (EPF, ESI) is a major trigger. If a contractor works only for you, follows a strict schedule, and uses your equipment, they are your employee.
Inconsistent Tax Withholdings:
Variances in TDS deductions among employees with similar salary structures, perhaps due to inconsistent management of investment declarations (Section 80C), HRA exemptions or mismatches between payroll data and employee ITR filings.
Late or Missing Payroll Tax Payments:
This is the easiest thing for any regulatory body (EPFO, ITD) to track. Delays in depositing statutory dues are instant red flags.
Discrepancies in Wage Reporting:
If there is a mismatch between the wages reported on your TDS returns (24Q) and the annual wages shown on the employees’ individual Form 16, it can trigger scrutiny from tax authorities.
High Employee Turnover or Complaints:
A surge in ex-employees filing claims or a high attrition rate often suggests underlying issues with the work environment, including incorrect final settlements or non-compliance with the Payment of Gratuity Act.
How To Do Payroll Audit - Steps-by-Step Guide
Here are the step-by-step internal audit procedures for payroll.
Step 1: Gather All Payroll Documentation
Start by collecting the complete document trail for a defined audit period (e.g., a financial year). If you are using a digital payroll management system, getting these records is easy. Make sure they are easily accessible and exportable.
- Employee forms and identity records
- Offer letters, contracts, amendments
- Salary structure documents, pay slips, payroll registers
- Statutory filings (PF, ESIC, PT, TDS, LWF)
- Time and attendance logs
- Proof of overtime, incentives, reimbursements
- Benefit summaries and deduction records
Step 2: Review Employee Classifications
Verify that every employee is correctly categorised according to the law.
Exempt vs. Non-Exempt Employees: Declaring who is eligible for overtime pay under the Minimum Wages Act and factory laws is crucial. Generally, those performing supervisory or managerial work may be treated differently from those doing purely clerical work.
Independent Contractors vs. Employees: Use the test of control (who dictates the work, schedule, tools, etc.) to confirm if the classification is legally sound.
Step 3: Verify Wage Calculations and Payments
This is the most crucial point. Verify whether the right amount is calculated and paid to the employees. Check:
- Basic, HRA, LTA, variable components
- State-wise minimum wages, which often change
- Overtime rates (1.5x, 2x depending on industry)
- Bonus, gratuity, and leave encashment calculations
- Accuracy of bank deposits vs. payroll register
Step 4: Audit Tax Withholdings and Deposits
This is a key area for the Income Tax Department and other statutory bodies. Verify:
- Monthly TDS calculations
- Quarterly Form 24Q filings
- PF and ESIC challans
- Professional Tax across multiple states
- FUTA/SUTA equivalents in Indian statutory systems (PF admin charges, ESIC contributions)
- Timeliness of deposits (especially for EPF and TDS)
Step 5: Examine Benefits and Deductions
Ensure that all deductions are authorised and accounted for correctly.
Health Insurance Premiums: Verify that the deducted amount matches the insurance provider’s invoice and the employee's authorisation.
Retirement Plan Contributions: Check that the employee's EPF contribution matches the calculation (12% of Basic + DA) and that the employer's share is correctly split between the EPF and EPS (Pension Scheme).
Garnishments and Child Support Orders: These must be meticulously managed according to specific court or government orders. Document the court order and ensure the deduction amount is correct.
Step 6: Cross-check Time and Attendance Records
Labour authorities focus heavily on how working hours are tracked, particularly for overtime.
Compare Timesheets with Payroll Records: Ensure the hours paid match the time recorded to avoid any wage theft claims from both sides.
Verify PTO, Sick Leave, and Vacation Accruals: Check that leave accrual and usage adhere to the company policy and the statutory requirements of the relevant Shops and Establishments Act.
Ensure Proper Documentation for Absences: All unpaid leaves or exceptions must be backed up by documented requests and approvals.
Step 7: Check for Compliance with Labour Laws
Go beyond taxes to ensure adherence to India's wide array of labour legislation.
Fair Labour Standards Act (FLSA) Compliance: While FLSA is US-based, its spirit is mirrored in India's Minimum Wages Act, Payment of Wages Act, and Factories Act. Focus on correct working hours, rest intervals, and overtime rules.
State-Specific Wage and Hour Laws: India has significant state variations, particularly with Professional Tax and state-specific minimum wages. Ensure you are compliant with the laws of all states where you have employees.
Record-Keeping Requirements: Confirm that all records are maintained for the required statutory period (often 6 to 8 years for tax purposes, and longer for certain labour records).
Step 8: Conduct Internal Testing and Spot Checks
Once you've done the full review, conduct small, focused internal tests to confirm your system's integrity.
- Redo wage calculations
- Check tax computations
- Inspect attendance-to-payroll flow
- Compare registers with bank statements
- Identify repeating errors. These usually indicate a deeper process issue
Step 9: Prepare an Audit Response Plan
Audits become stressful only if you have to rush through everything at the last minute. To prevent that, make sure you have:
- A designated audit coordinator
- A folder with every payroll document grouped logically
- Clear explanations for variances
- A timeline of your payroll process from onboarding to final settlement
If your auditor were to ask you for something and you could hand it over within seconds, it could change their entire tone.
Step 10: Address and Correct Any Issues
The most crucial step is fixing what you found in the payroll audit report.
Make Necessary Corrections Immediately: If an employee was underpaid, correct it in the next cycle and issue an apology.
File Amended Tax Returns if Needed: If you find an error in your TDS or EPF filings, file revised returns immediately.
Implement Processes to Prevent Future Errors: The correction shouldn't be a one-time fix. Update your master data, change the calculation logic in your payroll software.

After the Payroll Audit: How to Use the Results to Avoid Future Payroll Issues
You've completed the audit. Now, you must convert the findings into a stronger system.
How to Stay Perpetually Audit-Ready?
To make sure you're always ready for an audit, keep your payroll data clean, current, and easy to track all year long. When details like employee attendance, salaries, deductions, and important documents are kept organised, audits will just be a routine process.
A system like Mewurk helps maintain this order by automatically handling compliance updates and ensuring every record is accurate and immediately available
Conclusion
A payroll audit is an inevitable part of doing business, especially in a country with as dynamic a legal framework as India. You can choose to be obstinate by waiting for the inevitable audit notice to force you into a panicked, retroactive cleanup or be persistent by proactively building a transparent and compliant payroll system. The latter approach would safeguard your business from costly penalties and hint that your payroll foundation is solid enough to withstand any scrutiny with confidence.
FAQ
What does a payroll audit report include?
A payroll audit report should be heavy on facts. Here are the typical sections it must include:
- Audit period, scope and the person who did the review.
- Summary of findings (critical vs. minor).
- Reconciliations (payroll register → bank → tax filings).
- Statutory compliance checks (TDS, PF, ESI, PT).
- Exceptions, root causes and recommended corrections.
- Action plan, owner, and target date for fixes.
Download our free payroll audit report sample PDF here.
How long does a payroll audit take?
The duration of the payroll audit can depend on scale and scope. If it is a quick internal check for a small team in a single location, and you know the ins and outs of how to audit payroll, it could be completed in a day.
A Regulatory or external audit can range from 2 weeks to several months if extensive records or multiple years are involved.
What is the procedure for doing a payroll audit?
A payroll audit follows the steps we have explained in detail in the blog. It involves reviewing records, checking pay, and confirming compliance. If you want a quick PDF version of the procedure, download it here: [payroll audit procedures pdf]
Most Popular Post

Why Accurate Attendance and Leave Management Matters for Business Growth?
Read More →Why Accurate Attendance and Leave Management Matters for Business Growth?
How To Leverage Attendance Data For Better Workforce Management?
Read More →How To Leverage Attendance Data For Better Workforce Management?







